stochastic - If $X(t)$ is a WSS process with mean 5, what is the mean of $X(2t)$? - Signal Processing Stack Exchange

SOLVED: 3. X(t) is a wide sense stationary random process. For each process Xi(t) defined below, determine whether Xi(t) is wide sense stationary. (+)X=IX() (b) X2(t) = X(at) 4. Find the power
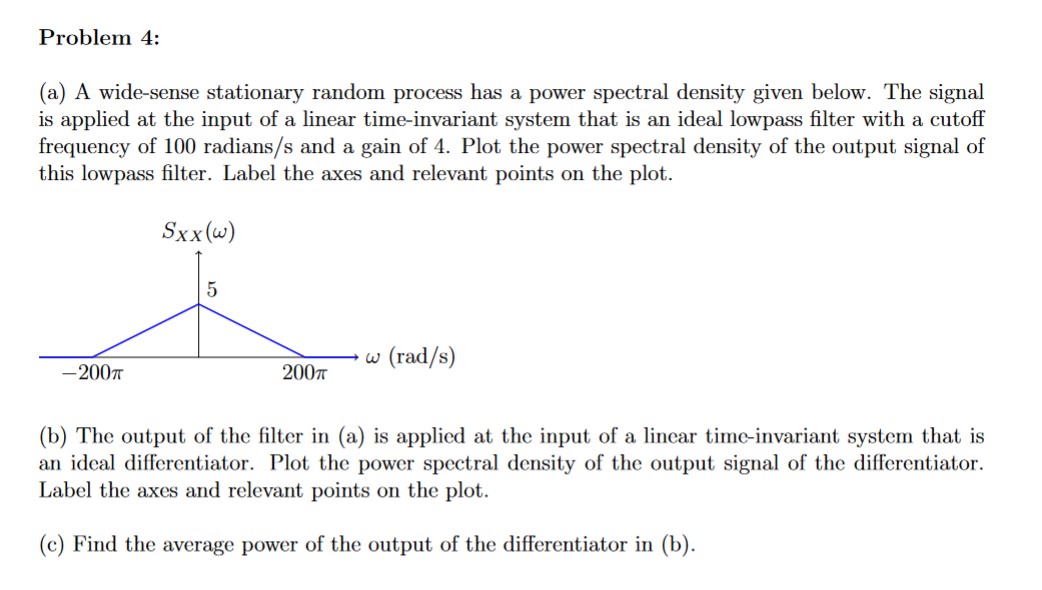
Let X(t) be a wide sense stationary random process with the power spectral density SX(f) as shown in Figure (a), where f is in Hertz (Hz). The random process X(t) is input







![Solved] The auto correlation function RX(τ) of a wide-sense stat Solved] The auto correlation function RX(τ) of a wide-sense stat](https://storage.googleapis.com/tb-img/production/21/02/F1_Shraddha_Shubham_22.02.2021_D%2013.png)


![PDF] The Wiener-Khinchin Theorem for Non-wide Sense stationary Random Processes | Semantic Scholar PDF] The Wiener-Khinchin Theorem for Non-wide Sense stationary Random Processes | Semantic Scholar](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/a11f2e217a0c0723024f69afa1d18b26950775ac/4-Figure2-1.png)